Memory & Learning
Objectives
At the end of this topic you will:
- describe how learning and memory has been studied in insects
- describe how learning and memory can operate on the behavioural level
- discuss how learning and memory can operate on the neural level
Outline
- Part 1: Learning and memory and the insect brain
- Part 2: Learning and memory and insect behaviour
Activities
Two mini-lectures discuss on the topics of learning and memory:
- Mini-lecture: Memory, learning, and the insect brain
- Mini-lecture: Memory, learning, and insect behaviour

Part 1: the Insect Brain
At the end of this section you will:
- How does learning and memory operate at the neural level?
- What brain areas do what in terms of learning and memory?
|
Learning and memory: involves changes in the connections between cells
- Memory and changes in synaptic strength can occur at many different levels of the insect brain
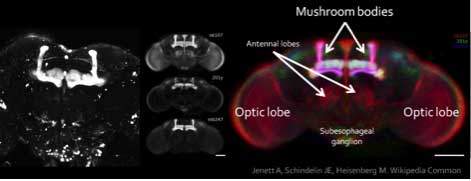
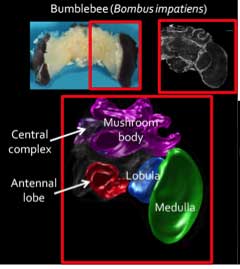
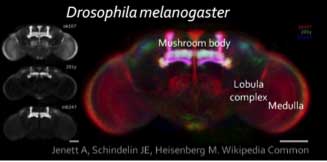
- Prominent areas where learning and memory have been shown to occur are:
- Antennal lobes
- Mushroom bodies
- Central complex
 |
 |
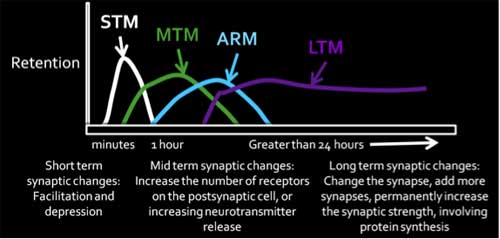
Different types of memory
Short-term (STM), middle-term (MTM), anesthesia resistant (ARM), and long-term (LTM) memory can induce different levels of changes in the connections between cells.
The synapse: How learning can happen
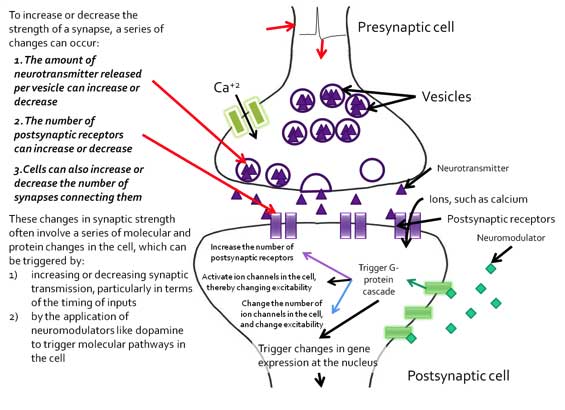
Numerous Drosophila mutants have been found where changes on the synaptic level have caused the flies themselves to have behavioural defects, such as poor learning and memory.
Much of this information is discussed at this website:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drosophila_melanogasterMuch of the material on Drosophila learning and memory is listed at the following book, if you can access it online:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bookshelf/br.fcgi?book=bnchm&part=A3577And a number of the genes involved in the Drosophila brain are listed here:
http://www.sdbonline.org/fly/brain/ahome.htmAnother tool researchers use to study Drosophila is borrowed from yeast, called the GAL4-UAS system, which is outlined below:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GAL4/UAS_system
Using this system, the certain genes can be turned on and off in specific areas of the brain.
References:
Heisenberg M (1998) What do the mushroom bodies do for the insect brain? Learn Mem 5:1-10.
Heisenberg M (2003) Mushroom body memoir: from maps to models. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:266-75.
The circuitry of learning
GAL4-UAS expression of green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the mushroom bodies of Drosophila melanogaster:
Different expression patterns of the mushroom bodies
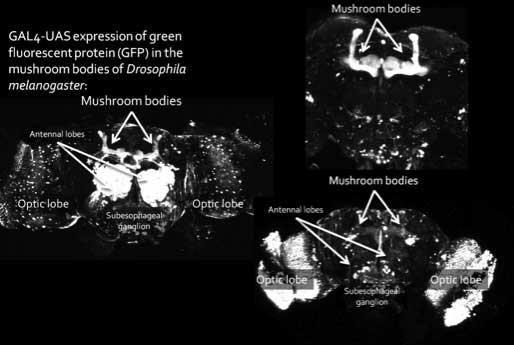
Mushroom bodies
The mushroom bodies have long been thought to be associated with learning and memory:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mushroom_bodies
Heisenberg M (1998) What do the mushroom bodies do for the insect brain? Learn & Mem 5: 1-10.
Heisenberg M (2003) Mushroom body memoir: from maps to models. Nat Rev Neurosci 4: 266-275.
Menzel R (1999) Memory dynamics in the honeybee. J Comp Physiol A 185: 323-340.
Menzel R (2001) Searching for the memory trace in a mini-brain, the honeybee. Learn & Mem 8: 53-62.
Recordings from neurons in the mushroom bodies have shown that the neurons can be plastic:
Cassenaer S, Laurent G (2007) Hebbian STDP in mushroom bodies facilitates the synchronous flow of olfactory information in locusts. Nature 448:709-713.
Mauelshagen J (1993) Neural correlates of olfactory learning in an identified neuron in the honeybee brain. J Neurophysiol 69:609-625.
The mushroom bodies actually also change and increase in volume with experience
Experience- and Age-Related Outgrowth of Intrinsic Neurons in the Mushroom Bodies of the Adult Worker Honeybee . (2001) Sarah M. Farris, Gene E. Robinson, and Susan E. Fahrbach. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21(16):6395-6404.
Vision affects mushroom bodies and central complex in Drosophila melanogaster. (1997) M Barth, M Heisenberg - Learning & Memory. Learn. Mem. 4: 219-229.
Other brain areas likely involved in learning and memory are the central complex:
Liu G, Seiler H, Wen A, Zars T, Ito K, Wolf R, Heisenberg M, Liu L (2006) Distinct memory traces for two visual features in the Drosophila brain. Nature. 439:551-556.
And the antennal lobe and the rest of the protocerebrum, though more research is needed to examine these possibilities.
Menzel R (1999) Memory dynamics in the honeybee. J Comp Physiol A 185: 323-340.
Menzel R (2001) Searching for the memory trace in a mini-brain, the honeybee. Learn & Mem 8: 53-62.
Ultimately, learning and memory can occur at many different levels of the brain, but much more research is needed to better understand how short, mid, and long term memory could occur in the insect brain, particularly considering all the connections we see:
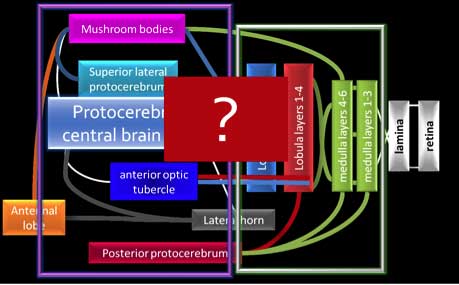
Activities
Find a paper on insect learning and read about how they trained the insects to learn, and be able to answer the following questions:
What are some of the molecular mechanisms underlying learning?
What brain areas change in volume with experience?
TOPIC REVIEWDo you know…?What are the mushroom bodies? |
 Go on to Part 2: insect behaviour
Go on to Part 2: insect behaviour

 Mini-lecture:
Mini-lecture: